Introduction: Tooth discoloration can be concerning, especially when it’s unclear whether it’s caused by hypocalcification or fluorosis. Both conditions can affect the enamel of your teeth, leading to noticeable white spots or discoloration. However, understanding the difference between these two and how they develop is key to addressing them effectively. In this post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about hypocalcification and fluorosis, their causes, treatments, prevention strategies, and more. If you’re asking, “Why are my child’s teeth chalky?” or “How to fix white spots on adult teeth,” we’ve got you covered.
Key Differences Between Hypocalcification and Fluorosis:
| Aspect | Hypocalcification | Fluorosis |
|---|---|---|
| Enamel Structure | Weakened, porous enamel | Potentially porous, but structurally sound in mild cases |
| Cause | Mineral deficiencies, genetic factors, high fevers | Excessive fluoride exposure during tooth development |
| Appearance | Chalky, soft, discolored enamel | White spots, streaks, or brown staining on enamel |
| Risk Factors | Premature birth, poor nutrition, high fever, genetics | Drinking fluoridated water, swallowing toothpaste |
| Treatment | Remineralization, bonding, veneers, crowns | Microabrasion, whitening, veneers, crowns |
| Prevention | Good nutrition, early dental care | Proper fluoride use, supervised brushing |
In the YouTube video above “ENAMEL HYPOPLASIA vs DENTAL FLUOROSIS” (published roughly 4 years ago), the presenter explains how enamel hypoplasia and dental fluorosis differ—both are enamel conditions but caused by distinct developmental issues. The video outlines how hypoplasia occurs when enamel doesn’t form fully during tooth development, while fluorosis results from excessive fluoride exposure during that growth phase. The comparison helps viewers understand signs, causes, and ways to differentiate these two enamel disorders
What is Hypocalcification?
Hypocalcification refers to the underdevelopment or weakening of the enamel, typically due to insufficient mineralization during tooth formation. This leads to a less durable and porous enamel structure. The process of enamel mineralization begins in childhood, with the help of ameloblasts, the cells responsible for enamel production. Any disruption in this process—whether due to nutritional deficiencies, trauma, or high fevers—can result in hypocalcification.
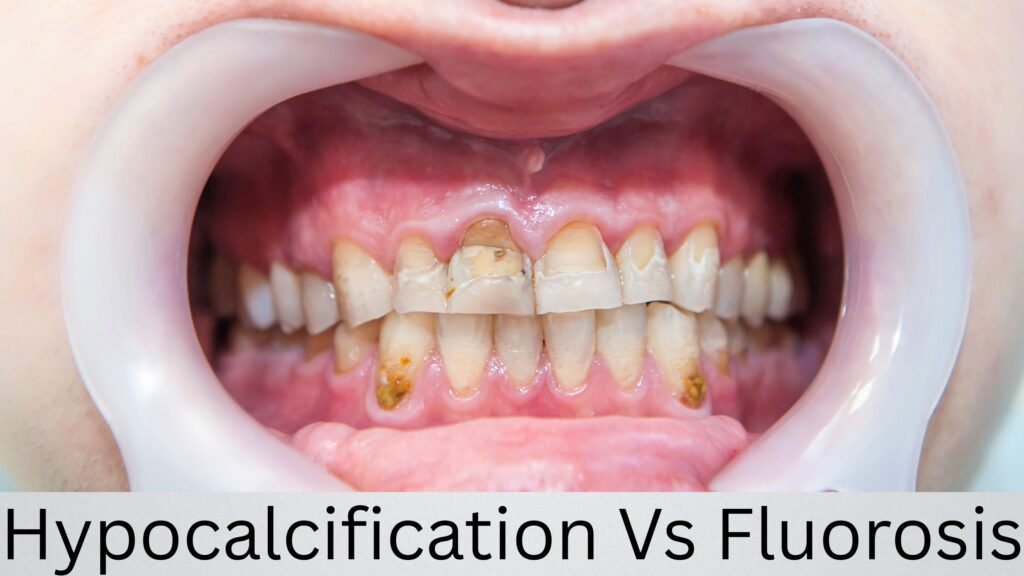
During enamel formation, the enamel is initially soft and translucent. Over time, it hardens as minerals like calcium and phosphate are deposited. However, if the mineralization process is disrupted, the enamel remains soft, leading to weakened spots that may appear chalky or discolored.
Causes of Hypocalcification
- Premature Birth: Preterm infants are more likely to experience enamel hypocalcification. This is often linked to calcium and phosphate deficiencies, which are crucial for enamel formation during the early stages of life.
- High Fever: High fever during critical developmental stages can disrupt ameloblast function, leading to incomplete enamel mineralization. This can cause the affected teeth to have a soft, porous appearance.
- Genetics: Some genetic conditions affect how enamel forms, resulting in inherent weakness or defects in the enamel.
- Poor Nutrition: A lack of essential nutrients, especially calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus, during tooth development can directly impact enamel strength.
Symptoms and Appearance of Hypocalcification
- Chalky Teeth: One of the first signs of hypocalcification is the appearance of chalky, white spots on the enamel, which feel softer to the touch.
- Discoloration: The affected enamel often appears more opaque or off-white, and the discoloration can vary in severity based on the extent of the damage.
- Tactile Feel: The enamel may feel rough or porous when you run your tongue over the surface. In some cases, it may even be slightly soft, which increases the risk of decay.
Treatment Options for Hypocalcification
- Remineralization Therapy: This involves applying fluoride compounds to the affected teeth, such as sodium fluoride or calcium phosphates. These compounds work by replacing lost minerals, thus strengthening the enamel and reducing porosity.
- Dental Bonding: For less severe cases, dental bonding can be used. A composite resin is applied to the tooth surface, restoring its appearance and providing some protection. However, bonding may need to be replaced over time, as it can chip or wear down.
- Veneers and Crowns: For more severe hypocalcification, veneers or crowns may be necessary. Porcelain veneers are used for cosmetic correction, while crowns offer a more comprehensive solution for significantly damaged teeth.
Prevention of Hypocalcification
- Nutrition: Ensuring adequate intake of calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus from a young age helps strengthen enamel. For expectant mothers, prenatal vitamins rich in these nutrients are essential for proper enamel development in the fetus.
- Early Dental Care: Regular dental visits from an early age help detect any enamel defects early, making it easier to address potential issues before they worsen.
What is Fluorosis?
Fluorosis occurs when there is excessive fluoride exposure during the tooth development phase, usually between the ages of 1-4 years. Fluoride is beneficial in small amounts as it helps with enamel remineralization, but too much fluoride can alter the structure of the enamel, leading to discoloration or weakened enamel. This condition typically affects both primary (baby) and permanent teeth.
Causes of Fluorosis
- Excessive Fluoride Exposure: Fluorosis is most commonly caused by ingesting too much fluoride during the critical period when the enamel is developing. This can occur through drinking water with high fluoride levels or swallowing toothpaste during brushing.
- Community Water Fluoridation: In the United States, fluoride is added to public drinking water to prevent tooth decay. However, excessive fluoride exposure, especially in areas with high natural fluoride levels, can lead to fluorosis.
- Fluoride Toothpaste: Parents should be cautious about the amount of toothpaste used by young children, as swallowing toothpaste can contribute to fluoride overexposure.
Symptoms and Appearance of Fluorosis
- White Spots or Streaks: In mild cases, fluorosis presents as small white spots on the teeth. As the condition progresses, the spots may become larger or form streaks along the enamel.
- Brown Staining: In more severe cases, the enamel can turn yellow or brown. This is often due to the increased porosity of the enamel, which allows stains to penetrate the surface.
- Decreased Enamel Strength: In extreme cases, the enamel becomes weak, which can lead to more significant dental issues such as fractures or wear.
Treatment Options for Fluorosis
- Microabrasion: This technique involves removing a thin layer of the affected enamel using a chemical and mechanical process. It’s often used for cosmetic purposes to eliminate mild fluorosis stains.
- Teeth Whitening: Whitening treatments may help lighten mild fluorosis stains. Hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide are commonly used to break down stains on the enamel surface.
- Veneers or Crowns: Like hypocalcification, severe fluorosis may require veneers or crowns for cosmetic improvement. Porcelain veneers are particularly effective for severe cases.
Prevention of Fluorosis
- Supervised Brushing: For children under the age of 6, parents should supervise brushing and ensure that only a small, pea-sized amount of toothpaste is used. A smear layer for babies is often recommended to avoid swallowing toothpaste.
- Balanced Fluoride Intake: Be mindful of the fluoride concentration in both drinking water and toothpaste. Regular dental checkups can help monitor fluoride exposure levels.
Differential Diagnosis
It’s essential to distinguish between hypocalcification and other conditions that cause white spots on teeth, such as enamel hypoplasia or the early signs of tooth decay. A professional dental evaluation is crucial for an accurate diagnosis, as the treatment for each condition may vary.
Psychological and Social Impact of Tooth Discoloration
Noticeable tooth discoloration can affect a person’s self-esteem, particularly in adolescents and adults. People with chalky teeth or stained enamel in children may feel self-conscious about their smile, leading to decreased confidence. It’s important to address these issues promptly to prevent potential emotional distress.
Conclusion:
Hypocalcification and fluorosis are two distinct conditions that can affect the enamel of your teeth. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for each can help you take the necessary steps to protect your enamel and maintain a beautiful, healthy smile. If you notice any signs of tooth discoloration, don’t hesitate to consult with your dentist for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Find Your Perfect Dentist
Easily book appointments with top-rated dentists in your area
Need Emergency Dental Care?
Get immediate help from verified dental professionals