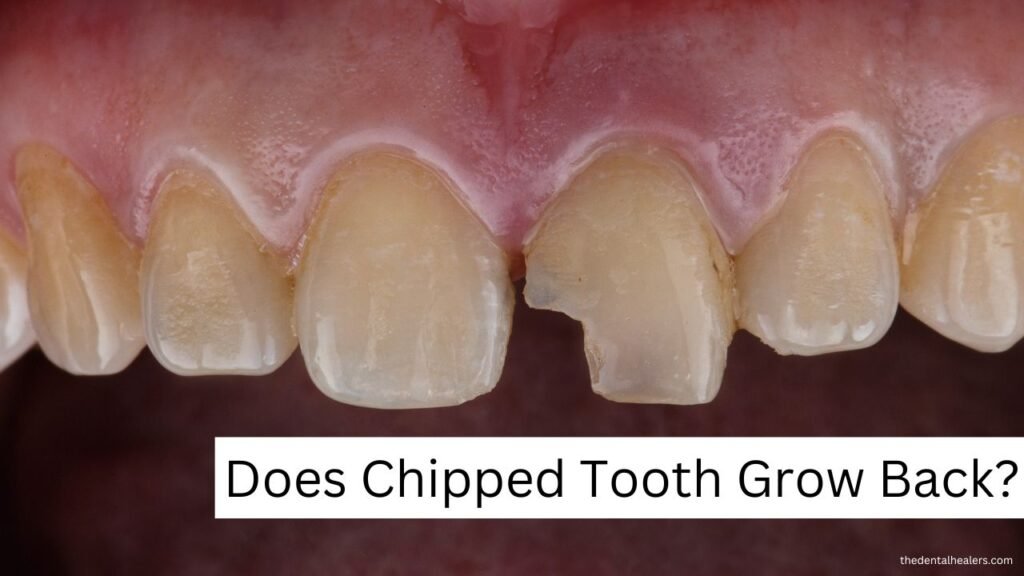
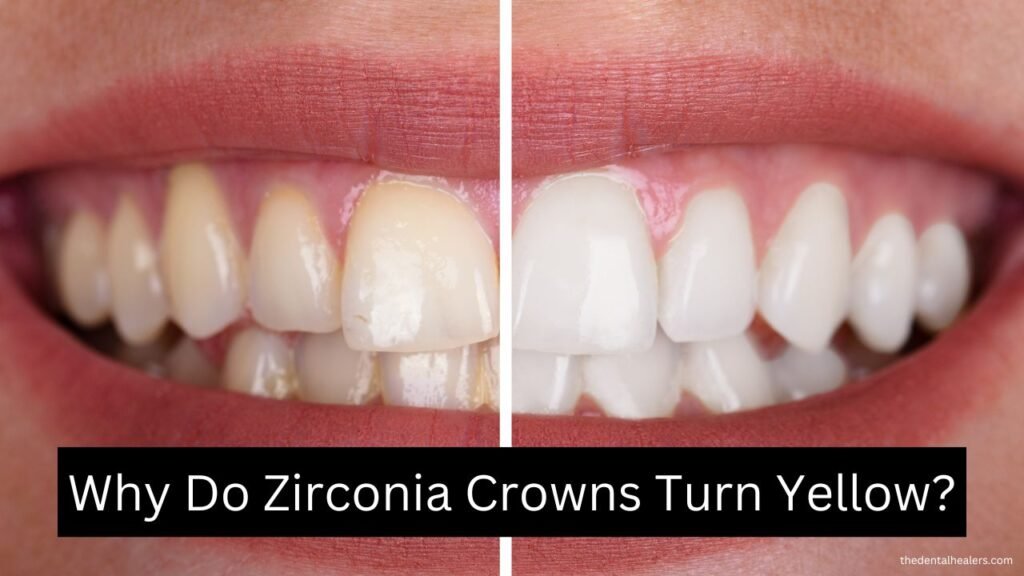
How Much Do Dental Caps Cost
A bright, healthy smile is often considered one of the best assets you can have. Dental caps, also known as crowns, play a crucial role in restoring both the functionality and aesthetics of your teeth. If you’re considering dental crowns, understanding the costs involved is vital for making an informed decision. This guide will walk […]